What’s the difference between type 1 and type 2 diabetes?
Many individuals know that diabetes is of two types, but not everybody is aware of what is the difference between the two. In both type 1 and type 2 diabetes, the levels of blood glucose go too high as the body fails to produce insulin (a hormone responsible for controlling blood sugar), or fails to use insulin properly. Even though the problem is similar to both types, they still have diverse causes and treatments.
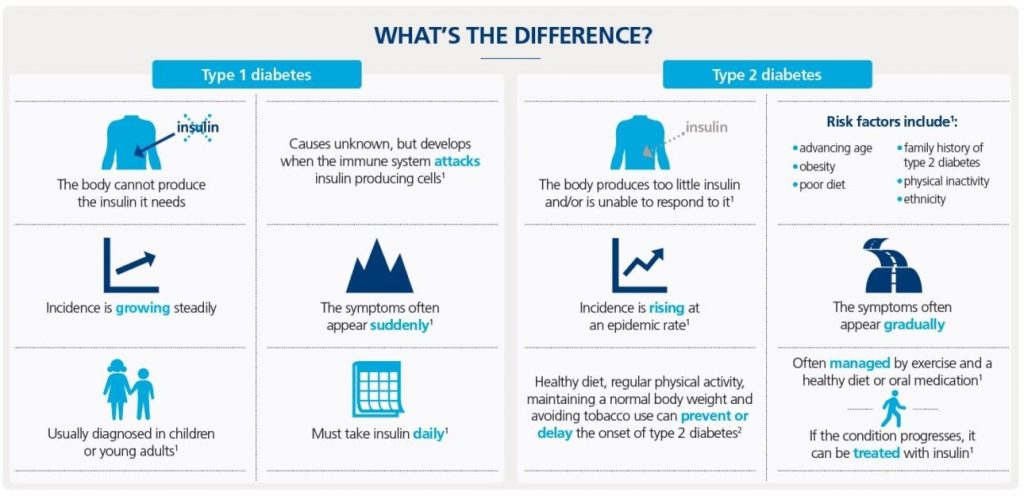
Type 1 Diabetes
One of the major differences between the two diabetes types is that type 1 diabetes is a hereditary disorder that frequently arises early in life, while type 2 is mostly diet-connected and is seen to develop over time. If a person suffers from type 1 diabetes, he or she has a damaged immune system, causing damaging insulin-producing cells in the pancreas.
The good news is now the medical science has evolved considerably and now recent interventions allow individuals having type 1 diabetes to avoid the effects of the ailment and live a comparatively “normal” life.
So, before moving further, let’s know the signs of type 1 diabetes:
Symptoms of type 1 diabetes include:
- Increased thirst
- Exhaustion and weakness
- Hazy vision
- Urinating more often
- Unexplained weight loss
Ways to treat type 1 diabetes:
Use insulin. As the body fails to produce it on its own, insulin has to be received in another way. Some of the ways can be regular injections or a wearable insulin pump.
Self monitoring blood sugar levels: Diabetics must be aware of healthy blood glucose levels and must keep regular track of his or her values. It is recommended to check it 4 to 10 times daily. A small blood glucose meter named a glucometer can be kept at home to measure sugar levels.
Maintain a balanced diet. It’s a must to count the carbs a person is having, ensure to have them consistently but not overeat. If a person is taking a fixed amount of insulin, it’s all the more important to take consistent carbs.
Exercise. Staying active is always an important component of health, but for people with type 1 diabetes, it can help keep blood sugar levels in check and cause your body to use the insulin more efficiently.
Diagnosing Type 1 Diabetes
A person must get his or her blood tests done in order to diagnose type 1 diabetes. One of these tests is an A1C screening. This screening test evaluates the blood glucose levels from the past 2-3 months and helps diagnose type 1, type 2 diabetes as well as prediabetes.
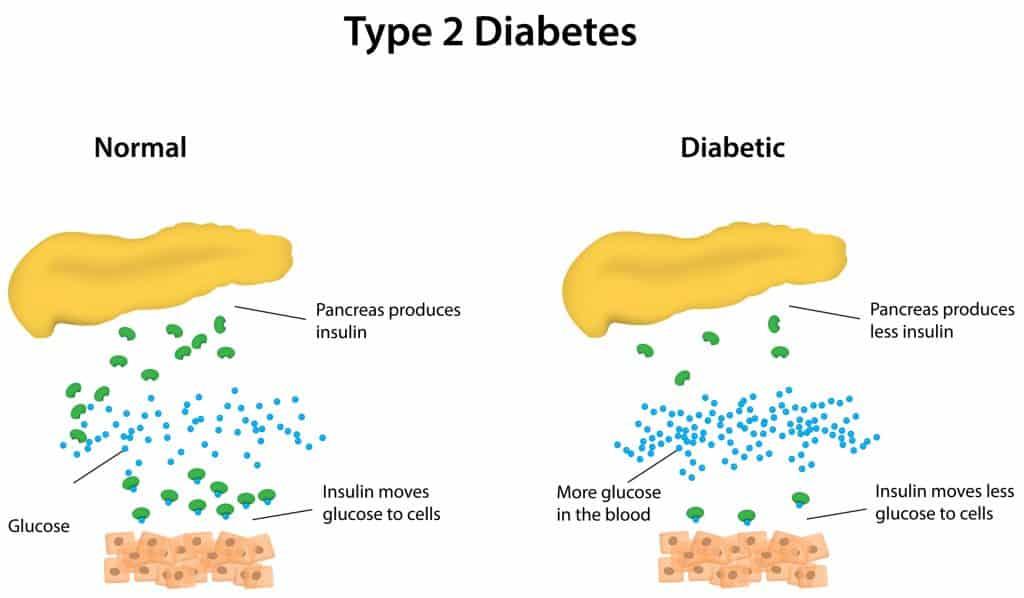
Type 2 Diabetes
Type 2 Diabetes is more common as compared to type 1, and is usually caused by lifestyle. In this type, a person’s body still forms a small quantity of insulin, however, it isn’t efficacious enough. The pancreas fails to sustain high blood glucose levels on account of a poor diet and physical inactivity. Individuals having type 2 diabetes have “insulin resistance,” implying their pancreas produces insulin however, their body does not identify it. The risk of developing type 2 diabetes is greater if a person’s diet contains a high number of carbs and fat but low fiber.
Signs of type 2 diabetes
- Tingling or numbness in hands or feet
- Too much thirst
- Urinating more often
- Tiredness
- Increased hunger
- Scratchy skin
- Blurred vision
Treatment
Contrasting type 1, individuals with type 2 diabetes often do not require using insulin, as their bodies still form a small quantity of it. Even though there exist some medicines such as Metformin to help reduce blood sugar, the prime ways to prevent type 2 diabetes may include:
- Self Monitor sugar levels. Checking the levels regularly, later on, becomes a significant part of every diabetic’s daily routine. It keeps them updated on how their levels are doing during the day and the person can also adjust food and activities consequently.
- A balanced diet. Consumption of fruits and veggies, lean proteins, and whole grains together with avoiding more than the irregular high-fat, high-sugar food is the primary step towards managing type 2 diabetes.
- Weight loss. If a person works on the consumption of healthier food choices and exercising, weight loss is guaranteed. Losing weight should be less about the number on the scale and it should be more about paying attention to the overall body and decreasing the strain on the pancreas.
- Staying physically active is very vital. It’s important to try different activities to look for a type of exercise a person enjoys and work it into the weekly routine.
The bottom line is:
Type 1 diabetes is a hereditary disorder that classically emerges early in life, whereas type 2 diabetes develops with time, and is mainly because of diet. In both cases, a person’s body does not form a sufficient amount of insulin to properly control the levels of blood sugar, however for varied reasons. If a person notices any signs, he or she may get tested for diabetes using an A1C screening, which examines the blood glucose for the past 2-3 months.





